File System Heirarchy
Filesystem Hierarchy Standard(FHS) defines the way in which the directories are present in the linux .
All files and directories are present under " / " directory ( / is the root directory).
In linux each directory inside / (root directory) will have a perticular action to perform such as home directory will have local users account information.
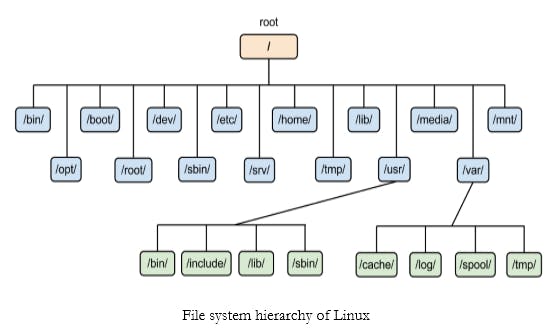
/ -->Main directory which contains all subdirectories
/bin -->Contains useful commands used by non-privileged user , for example cp,mv,rm,cat ..etc.
/boot -->Contains all files related to boot loader e.g., kernels, initrd.
/dev -->It includes terminal devices , usb , or any device that is attached to the system. For example: /dev/tty1, /dev/usbmon0
/etc -->It contains configuration files required by all the programs. For example: /etc/resolv.conf, /etc/logrotate.conf
/sbin –->Like /bin, /sbin also contains binary executables but the linux commands located under this directory are used typically by system aministrator, for system maintenance purpose. For example: iptables, reboot, fdisk, ifconfig, swapon
/proc –>Contains information about system process.This is a pseudo filesystem contains information about running process. For example: /proc/{pid} directory contains information about the process with that particular pid.
/var –>This includes system log files (/var/log) , packages and database files (/var/lib) , emails (/var/mail) , print queues (/var/spool) ,lock files (/var/lock) , temp files needed across reboots (/var/tmp)
/tmp –>Directory that contains temporary files created by system and users.Files under this directory are deleted when system is rebooted.
/usr –> Contains binaries, libraries, documentation, and source-code for second level programs.
/usr/bin contains binary files for user programs.
If you can’t find a user binary under /bin, look under /usr/bin.
For example: at, awk, cc, less, scp
/usr/sbin contains binary files for system administrators. If
you can’t find a system binary under /sbin, look under /usr/sbin.
For example: atd, cron, sshd, useradd, userdel
/usr/lib contains libraries for /usr/bin and /usr/sbin
/usr/local contains users programs that you install from
source. For example, when you install apache from source, it
goes under /usr/local/apache2
/home –>Home directories for all users to store their personal files. For example: /home/john, /home/nikita
/lib –>Contains library files that supports the binaries located under /bin and /sbin .Library filenames are either ld or lib.so.* For example: ld-2.11.1.so, libncurses.so.5.7
/opt –->opt stands for optional.Contains add-on applications from individual vendors. Add-on applications should be installed under either /opt/ or /opt/ sub-directory.
/mnt –>Temporary mount directory where sysadmins can mount filesystems.
/media –> Removable Media Devices.Temporary mount directory for removable devices. For examples, /media/cdrom for CD-ROM; /media/floppy for floppy drives; /media/cdrecorder for CD writer
/srv –> srv stands for service.Contains server specific services related data. For example, /srv/cvs contains CVS related data.